Closing the Gaps Between Common Core and The CAFE Menu
Join Our Community
Access this resource now. Get up to three resources every month for free.
Choose from thousands of articles, lessons, guides, videos, and printables.
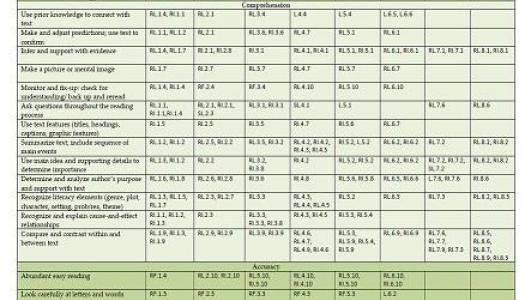
As I worked to align the CAFE menu with the Common Core standards for each grade level, I learned a lot about the Common Core standards and what is expected at each level for students to be successful. I saw gaps in the Common Core that I thought were filled nicely by the strategies in the CAFE menu, and I saw standards in the Common Core that are not addressed in the CAFE menu. My original thinking was that the CAFE menu should be adapted to include all standards in the Common Core. This way we would know we were addressing everything in the menu. Then, when I thought about what that would look like, I realized it would not only be hard to do, it would change the purpose of the CAFE menu and the reason we use it in teaching our students.
The purpose of the CAFE menu is to help students understand and master different strategies used by successful readers (Boushey & Moser, 2012). The purpose of the Common Core was to provide a clear framework for all teachers and parents in order to prepare K-12 students for college and careers (NGA Center and CCSSO, 2011). Although both are in line to enhance student performance, they are not one and the same. The Common Core language arts standards include ALL standards that must be taught for each grade level, K-12. The CAFE menu focuses specifically on reading strategies, not writing and speaking. It provides a resource for students to use in tackling challenges that interrupt their reading and comprehension. Therefore, even though the menu has been aligned with Common Core, it is not all encompassing and teachers must still visit the Common Core standards to ensure they are teaching everything required to produce successful students.
Here are a few concepts not included in the CAFE menu that stood out at many grade levels:
Taking compare and contrast a step further:
- Explain major differences between fiction and non-fiction, drawing on a wide reading of a range of text types
- Basic features of print
- How words and phrases (e.g., regular beats, alliteration, rhymes, repeated lines) supply rhythm and meaning in a story, poem, or song
- Differences between poems, drama, and prose, and refer to the structural elements of poems (e.g., verse, rhythm, meter) and drama (e.g., casts of characters, settings, descriptions, dialogue, stage directions) when writing or speaking about a text
- Compare and contrast the treatment of similar themes and topics (e.g., opposition of good and evil) and patterns of events (e.g., the quest) in stories, myths, and traditional literature from different cultures.
- Compare and contrast a firsthand and secondhand account of the same event or topic; describe the differences in focus and the information provided.
- Compare and contrast stories in the same genre (e.g., mysteries and adventure stories) on their approaches to similar themes and topics.
- Use of figurative language such as metaphors and similes
- Analyze how a particular sentence, paragraph, chapter, or section fits into the overall structure of a text and contributes to the development of the ideas
- Integrate information presented in different media or formats (e.g., visually, quantitatively) as well as in words to develop a coherent understanding of a topic or issue In addition to the ideas mentioned here, the Common Core has a set of writing and a set of speaking & listening standards for each grade level.
References
Boushey, G., & Moser, J. (2012). CAFE . Retrieved March 22, 2012, from The Daily Cafe
NGA Center and CCSSO. (2011). About the Standards. Retrieved March 22, 2012, from Common Core State Standards Initiative: http://www.corestandards.org/about-the-standards Download this article: Closing the Gaps Between The Common Core and The CAFE Menu